Computer Network Topology with Formulas (Number of Links, Ports, and Cable Length) & Comparison Table
Network topology defines how devices (nodes) are connected in a network. Below are the formulas for number of links, ports per device, and total cable length for different topologies.
1. Bus Topology
- Description: A single central cable (backbone) connects all devices.
- Formulas:
- Number of Links (Cables): L=1
- Number of Ports per Device: P=1
- Total Cable Length: Length=(N-1)XD
2. Star Topology
- Description: All devices connect to a central hub or switch.
- Formulas:
- Number of Links (Cables): L=N
- Number of Ports on Hub/Switch: P=N
- Total Cable Length: Length=N×D
3. Ring Topology
- Description: Each device connects to exactly two other devices, forming a closed loop.
- Formulas:
- Number of Links (Cables): L=N
- Number of Ports per Device: P=2
- Total Cable Length: Length=N×D
4. Mesh Topology
- Description: Each node connects to every other node.
- Formulas:
- Number of Links in Full Mesh: L=N(N−1)/2
- Number of Links in Partial Mesh: L<N(N−1/)2
- Number of Ports per Device in Full Mesh: P=N-1
- Total Cable Length (Approximate): Length=L×D
5. Tree Topology
- Description: A hierarchical structure with a root node and branches.
- Formulas:
- Number of Links (Cables): L=N−1
- Number of Ports per Device (Varies based on branching factor BB): P=B
- Total Cable Length: Length=(N−1)×D
6. Hybrid Topology
- Description: A combination of two or more topologies.
- Formulas:
- Number of Links: Depends on the combination of topologies
- Number of Ports: Varies based on structure
Comparison Table of Network Topologies
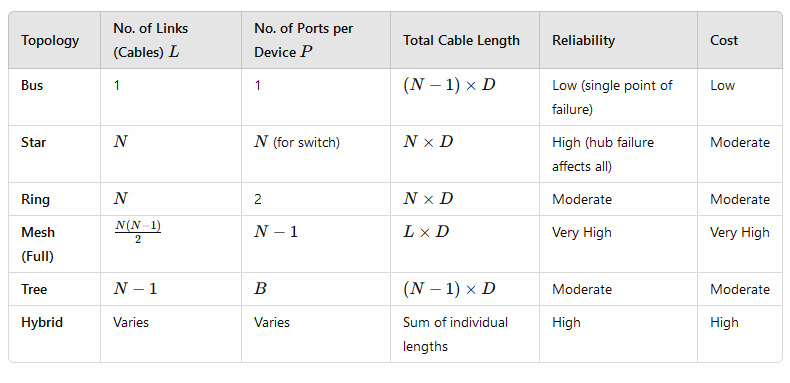
Conclusion:
- Bus topology is simple and cost-effective but unreliable.
- Star topology is widely used due to its easy troubleshooting.
- Ring topology is less used due to slower performance in large networks.
- Mesh topology provides high reliability but is expensive.
- Tree topology is used in large networks like the internet.
- Hybrid topology combines benefits of different topologies.




