1. Medium Access Control can be categorized into…
- A. Two types
- B. Three types
- C. Four types
- D. Five types
- E. None of the above
Ans-B. Three types
Explanation:- Medium Access Control is three types

2. In which type of medium access control sender station can send data frame any time…
- A. Random Access Control
- B. Controlled Access Control
- C. Channelization Protocol
- D. Token Passing
- E. None of the above
Ans-A. Random Access Control
3. CSMA full form is…
- A. carrier sense multiple access
- B. controlled sense multiple access
- C. common sense multiple access
- D. control sense mutual access
- E. None of the above
Ans-A. carrier sense multiple access
4. CSMA/CD full form is…
- A. carrier sense multiple access/collision detection
- B. controlled sense multiple access/control detect
- C. common sense multiple access/collision detection
- D. control sense mutual access/collision detection
- E. None of the above
Ans- A. carrier sense multiple access/collision detection
5. Listen before sending is principle of…
- A. carrier sense many access
- B. controlled sense multiple access
- C. carrier sense multiple access
- D. control sense mutual access
- E. None of the above
Ans- C. carrier sense multiple access
ARP,RARP,ICMP MCQs for exams
6. The time in which collision can take place is called…
- A. Jamming time
- B. Collision time
- C. Propagation time
- D. Vulnerable time
- E. None of the above
Ans- D. Vulnerable time
7. The Vulnerable time of Pure Aloha is (If Transmission time is TT and Propagation time is TP)…
- A. TT
- B. 2*TT
- C. TP
- D. 2*TP
- E. None of the above
Ans- B. 2*TT
8. The Vulnerable time of Slotted Aloha is (If Transmission time is TT and Propagation time is TP)…
- A. TT
- B. 2*TT
- C. TP
- D. 2*TP
- E. None of the above
Ans- A. TT
9. The Vulnerable time of CSMA is (If Transmission time is TT and Propagation time is TP)…
- A. TT
- B. 2*TT
- C. TP
- D. 2*TP
- E. None of the above
Ans- C. TP
10. The time for which a station wait after collision takes place is called…
- A. Vulnerable Time
- B. Back of Time
- C. Propagation Time
- D. Time out Timer
- E. None of the above
Ans- B. Back of Time
11. After collision detection in CSMA/CD signal send by detecting station is…
- A. Jam Signal
- B. Preamble Signal
- C. Sample Signal
- D. Ping Signal
- E. None of the above
Ans- A. Jam Signal
12. CSMA/CA is used to avoid collision in…
- A. Wireless Network
- B. Wired Network
- C. Ethernet Network
- D. Token Ring Network
- E. None of the above
Ans- A. Wireless Network
13. Efficiency of Pure Aloha is…
- A. 2*G*e-2G
- B. G*e-G
- C. G*e-2G
- D. G*e-4G
- E. None of the above
Ans- C. G*e-2G
14. Efficiency of Slotted Aloha is…
- A. 2*G*e-2G
- B. G*e-G
- C. G*e-2G
- D. G*e-4G
- E. None of the above
Ans- B. G*e-G
15. Back off time (if Kth collision occur) of Pure Aloha is…
- A. 2K * Time slot (where K value is 0 to 2k-1 and Time slot can be RTT,TP or TT )
- B. K * Time slot (where K value is 0 to 2k-1 and Time slot can be RTT,TP or TT )
- C. 4K * Time slot (where K value is 0 to 2k-1 and Time slot can be RTT,TP or TT )
- D. 8K * Time slot (where K value is 0 to 4k-1 and Time slot can be RTT,TP or TT )
- E. None of the above
Ans- B. K * Time slot (where K value is 0 to 2k-1 and Time slot can be RTT,TP or TT )
ARP,RARP,ICMP MCQs for exams
16. In Slotted Aloha Frame is send by sender…
- A. Any Time
- B. After a given time period called Slot time (Transmission time TT or Vulnerable time)
- C. In a given time period called Propagation time
- D. In a given time period called 2 * Propagation time
- E. None of the above
Ans-B. In a given time period called Slot time (Transmission time TT or Vulnerable time)
17. Efficiency of Pure Aloha in percentage is…
- A. 36.8
- B. 54.4
- C. 18.4
- D. 13.6
- E. None of the above
Ans- C. 18.4
18. Efficiency of Slotted Aloha in percentage is…
- A. 36.8
- B. 54.4
- C. 18.4
- D. 13.6
- E. None of the above
Ans- A. 36.8
19. A access method in CSMA for which sending station sense link continue sly …
- A. 1-Persistent
- B. Non-Persistent
- C. O-Persistent
- D. L-Persistent
- E. None of the above
Ans- A. 1-Persistent
20. A access method in CSMA for which sending station not sense link continue sly and wait random amount of time for sending frame…
- A. 1-Persistent
- B. Non-Persistent
- C. O-Persistent
- D. L-Persistent
- E. None of the above
Ans- B. Non-Persistent
21. A access method in CSMA for which sending station sense link continue sly and wait random amount of time for sending frame…
- A. 1-Persistent
- B. Non-Persistent
- C. O-Persistent
- D. P-Persistent
- E. None of the above
Ans- D. P-Persistent
22. In Pure Aloha if nth collision take place than random amount of time station waits for sending next frame…
- A. 2n * Time slot
- B. (0 to 2n-1) * RTT
- C. 4n * Time slot
- D. 8K * Time slot (where K value is 0 to 4k-1 and Time slot can be RTT,TP or TT )
- E. None of the above
B. (0 to 2n-1) * RTT
ARP,RARP,ICMP MCQs for exams
23. In a Ethernet network if link bandwidth is 1Mbps over a 2Km cable and speed of signal bits are 2000 Km/sec than minimum frame size for this network is…
- A. 4000 bits
- B. 2000 bits
- C. 8000 bits
- D. 1000 bits
- E. None of the above
B. 2000
Solution:- Ethernet uses CSMA/CD
Minimum frame size of CSMA/CD = 2* TP*Bw
First we have to find Propagation time=Distance / Speed
TP= 2000/2000* 103 =1msec
Bandwidth= 1Mbps
Putting these values to above formula
Frame size= 2x1x10-3x106=2000 bits
24. A CSMA/CD network in working in figure shown below
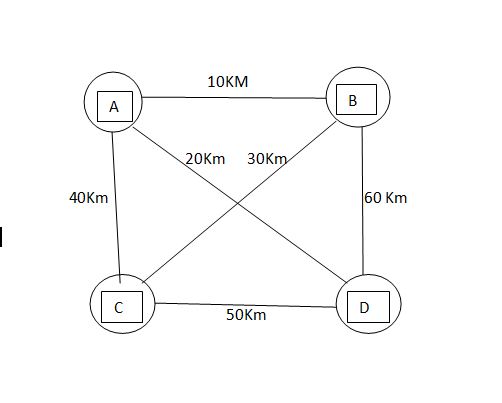
If the bandwidth of link is 2Kbps and speed of signal is 30Km/sec then minimum frame size is…
- A. 4000 bits
- B. 2000 bits
- C. 8000 bits
- D. 1000 bits
- E. None of the above
A. 4000 bits
Solution:- In CSMA/CD network we are using maximum distance. In above diagram we are using 60Km distance
Minimum frame size of CSMA/CD = 2* TP*Bw
First we have to find Propagation time=Distance / Speed
TP= 60×103/30×03 = 2 sec
Bandwidth= 2 Kbps
Putting these values to above formula
Frame size= 2x2x103=4000 bits

1 thought on “Medium Access Control-MAC MCQ in Data link Layer”